
Moreover, process costing also requires the adjustment of costs for opening and closing inventory, normal and abnormal spoilage, and transfers between production stages. This can make the accounting process more time-consuming, error-prone, and cumbersome. Can you imagine having to determine the cost of making just ONE lego when we can make 1.7 million legos per hour? Accountants compute the cost per unit by first accumulating costs for the entire period (usually a month) for each process or department. Second, they divide the accumulated costs by the number of units produced (tons, pounds, gallons, or feet) in that process or department. In average cost method, the cost of opening WIP is added to material, labour and overhead costs incurred process costing system during the period.
Total ending WIP amount & Total cost allocation
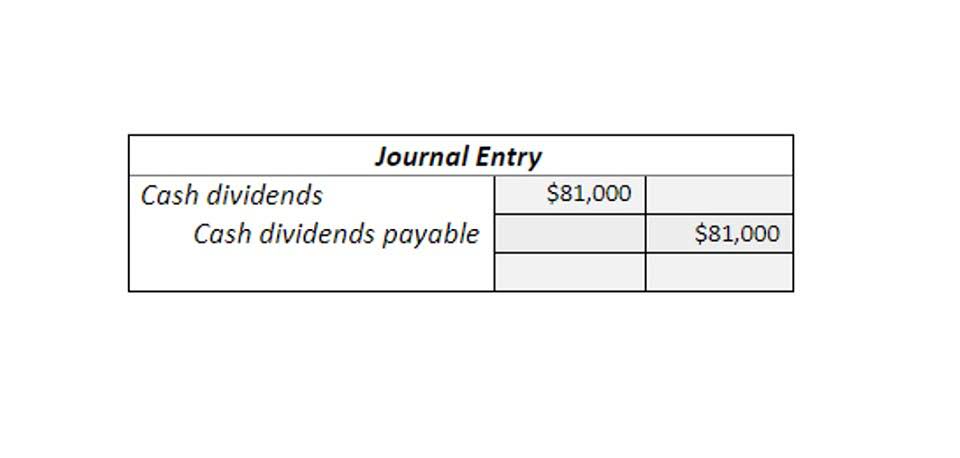
Production Order – In process costing work is performed for stock purpose on the continuous basis. The joint products cannot be identified as separate products up to a certain stage in manufacturing. Costs incurred prior to this stage are joint https://continentallacres.com.br/continentallacres/ costs, and costs thereafter are called subsequent costs. The cost before the separation stage has to be distributed to each product.

Process Costing vs. Other Costing Methods
Overheads can be factory overheads, office overheads and selling and distribution overheads. All these overheads expenses are distributed or apportioned among all the processes on a reasonable and relevant base. The payment of wages or salaries to the workers engaged to carry out the work of that particular process is debited to that process for which it is paid.
- In this approach, each job order becomes an independent cost analysis unit, where all necessary resources—such as materials, direct and indirect labor, and general manufacturing costs—are assigned in detail.
- The textile industry can also serve as an example, specifically in the production of basic t-shirts.
- When every dollar counts, Fishbowl equips you with the tools to take control of process costing, optimizing production schedules and maximizing profitability.
- For the sake of simplicity it is assumed that there is no work in process at the end of the accounting period.
- If production is not homogeneous, as in the case of foundries making castings of different sizes and shapes, the average cost may give an incorrect picture of cost.
- Assigning these productcosts to individual products remains an important goal for processcosting, just as with job costing.
Process costing in modern manufacturing – the software advantage
For instance, in a batch of paint, every gallon “shares” the total cost of materials used in production. Process costing is a cost accounting method used to assign production costs in industries where large quantities of identical products are manufactured. Instead of tracking expenses for individual units, costs are accumulated for each stage of production and then evenly distributed across all finished goods. This approach simplifies cost management and provides a clear view of production expenses.
- Beginning WIP units are the number of units that have been started, but not finished, at the beginning of a given month.
- Costs are accumulated at each department or process, including direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead, all assigned to specific production departments.
- That is, the production and processing ofproducts begin in Department A. From Department A, products go toDepartment B.
- Companies making paint, gasoline, steel, rubber, plastic, and similar products use process costing.
- The sticks are dried, and then sent to the packaging department, where the sticks are embossed with the Rock City Percussion logo, inspected, paired, packaged, and shipped to retail outlets such as Guitar Center.
- Main Product may be By-Product of Other Firm – A main product of one firm may be a by-product of another firm, which may be available in the market at prices which are lower than the cost of the first mentioned firm.

Remember to estimate the percentage complete based off of value, not quantity. If the total value of the Direct Materials added in Dept A is $23.44 and approximately $14.07 worth of materials have been added (on average) at month-end. Then you would enter 60% for the WIP percentage complete under Direct Materials. This quantity tells you how many units were partially started at the beginning of the period, and how many brand new units were transferred into the department.
More articles on Accounting

If the costs incurred during the period is Rs. 14,400, the cost per equivalent unit will be Rs. 2, i.e., Rs. (14,400/7,200). (vi) When total cost of the process is divided by the units produced in that process it results into per unit cost of that process. (b) Determine the total accumulated cost relating to the process, i.e., cost transferred + cost introduced in the process (material, labour and proportionate share of overhead) – scrap value of normal loss. Abnormal loss refers to the loss which is not inherent to manufacturing operations.
What is an example of a process costing company?

A process costing system also aims to ensure uniformity in reporting. By using this system, each department tracks its own costs and all those costs will be rolled up to arrive at a total cost to produce a specific number of products. Since all the expenses have to be summed up in a process costing system, they have to be reported in the same manner which brings about uniformity to reports and makes tracking costs over time easier. A process costing system accumulates costs when a large number of identical units are being produced. In this situation, it is most efficient to accumulate costs at an aggregate level for a large batch of products and then allocate them to the individual units produced.
Cost of each unit is calculated at the end of the period (commonly one month or after one week as the case may be). Cost per unit (average) is obtained by dividing the total cost applicable to a production department during a particular period by the total number of units produced during that period. The weighted average method combines costs from current Suspense Account and previous production periods.
Allocating Costs to Production Units
Once products are deliveredto retail stores, product costs are transferred from finished goodsinventory to cost of goods sold. Capabilities to monitor and report operational costs, labor, and other expenditures related to production processes, an accurate analysis of manufacturing costs can be generated for process costing. MRP (Materials Requirement Planning) software encompasses all manufacturing resources.

No responses yet